Study: Remote Patient Monitoring Enables Outpatient Bariatric Surgery with High Success Rates
The Current Health Clinical Research team, in collaboration with partners from the Defense Health Agency, has recently completed a study on the feasibility of outpatient bariatric surgery with the support of remote patient monitoring. The study’s main objective was to evaluate a novel remote patient monitoring protocol for same-day laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (SG) bariatric surgery in an outpatient setting while utilizing Current Health remote monitoring technology to manage postoperative care.
SG is the most performed bariatric procedure in the United States, since eclipsing the gastric bypass in 2013. It accounts for 59.4% of all bariatric procedures (estimated to be 256,000) in 2019. Despite being performed in high numbers, and the cost savings and safety profile associated with outpatient surgery, the vast majority of SG continue to be performed in an inpatient setting. Our pilot study demonstrated a workable protocol for RPM in sleeve gastrectomy that achieved high adherence to monitoring, even in patients traditionally considered higher risk, such as those with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Bariatric surgery is a highly effective treatment option for obesity, which typically involves a one-night hospital stay, followed by an extended period of postoperative recovery. Because bariatric surgery is elective, it’s one of the first procedures to be canceled when inpatient capacity is needed for essential surgeries. The use of remote patient monitoring technology has the potential to reduce the need for hospital stays altogether for many patients and reduce costs by allowing more procedures to shift to an ASC or outpatient environment. This study aimed to demonstrate the feasibility of an outpatient bariatric surgery program with remote patient monitoring support.
Read the full article: Outpatient Bariatric Surgery with Remote Patient Monitoring: A Feasibility Study
A Same-Day Protocol for Sleeve Gastrectomy
Remote patient monitoring technology has the potential to support outpatient bariatric surgery by providing patients with real-time monitoring of their vital signs, wound healing, and other relevant parameters. This technology allows healthcare providers to track patients’ progress and intervene quickly if any complications arise.
Existing literature about leveraging RPM for bariatric surgery has pointed to challenges with intermittent monitoring adherence, language accessibility, and in-home WiFi requirements. This study sought to remove those barriers “by using continuous in-home monitoring with embedded cellular transmission of patient data and the ability to provide educational material, surveys and prompts in multiple languages. Patients were not required to actively engage with the continuous monitoring devices or have a home WiFi connection for vital sign transmission. We also built-in automated prompts and surveys to increase patient engagement and adherence.”
“Does improved technology lead to higher patient adherence to monitoring?”
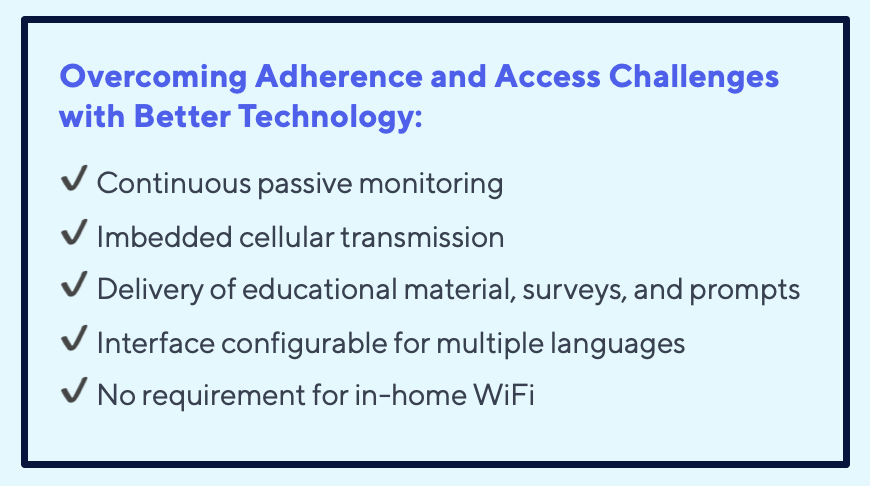
The study’s findings: safety, adherence, and cost savings
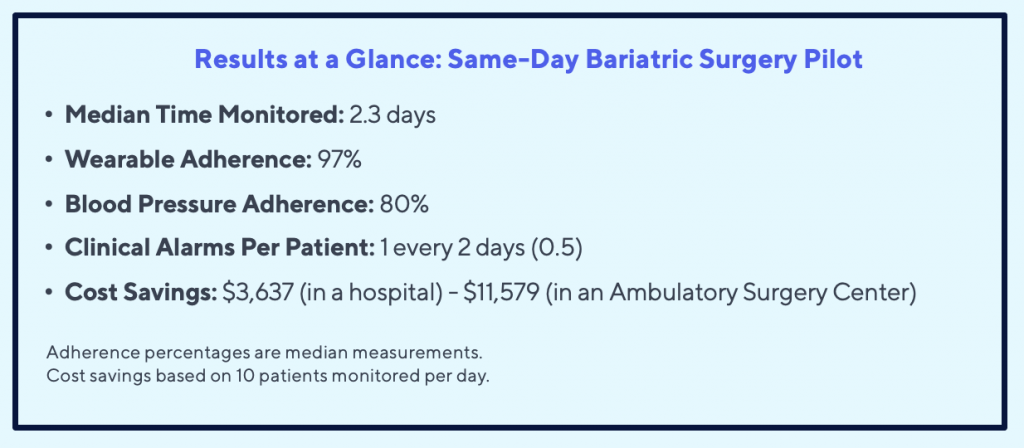
The study showed that outpatient bariatric surgery with remote patient monitoring support is a feasible and safe approach for selected patients. The study included 20 patients who underwent bariatric surgery in an outpatient setting with the Current Health platform. Their experiences were compared to 53 patients who were inpatient for their procedure. The patients had similar outcomes in terms of complications and readmissions compared to traditional inpatient bariatric surgery.
It is important to note that these cost savings were achieved by shifting patients from the inpatient to outpatient setting. During the study period, DHA only allowed outpatient SG if it also included remote patient monitoring, therefore any cost savings is directly attributable to the program. In other settings, cost savings is dependent on enrolling patients in the program who would otherwise have an inpatient procedure in the absence of a remote monitoring program.
Conclusion
In conclusion, outpatient bariatric surgery with remote patient monitoring is a promising approach that has the potential to reduce costs and enhance patient satisfaction. The protocol was a success, demonstrating high levels of adherence and reliability, and the potential for significant cost savings. Further studies are needed to evaluate similar protocol for other surgical procedures and higher risk patient populations.


![[Webinar Recording]This Way Home: Top 10 Predictions for Care at Home in 2025](https://www.currenthealth.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/DSG-846-JAN-WEBINAR-LINKEDIN-16_9-AD2-P2.jpg)